When selecting a cable gland, it’s essential to understand the differences between double compression and single compression types. These components are crucial in ensuring the safety and reliability of electrical installations by providing strain relief and environmental protection to cables. Choosing the right cable gland is critical for ensuring the safety, reliability, and longevity of your electrical installations. Whether you need the simplicity and cost-effectiveness of a single compression cable gland for standard applications or the enhanced protection and durability of a double compression cable gland for demanding environments, making an informed decision is key.
What is Single Compression Cable Gland?
A single compression cable gland is a type of cable gland that provides a seal and strain relief at a single point where the gland body tightens around the outer sheath of the cable. This type of gland is used to secure and protect cables as they pass through enclosures, panels, or equipment, providing basic protection against dust and moisture. A single compression cable gland, also known as a single compression cable connector. Single compression cable glands are suitable for general-purpose applications in industrial and commercial settings where moderate environmental protection is sufficient.
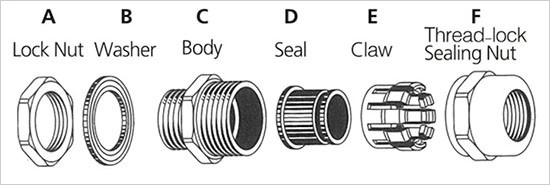
The typical components of a single compression cable gland:
- Gland Body: The main body of the cable gland that houses the other components and provides the overall structure.
- Flat Washer: A flat washer is located under the head of a nut or bolt in order to provide a smooth bearing surface. Additionally, it spreads out the fastener load to a wider area.
- Lock Nut: Used to secure the cable gland to the equipment or panel if it doesn’t come with a pre-threaded entry.
- Rubber Washer: It is a ring made of rubber that is used in mechanical devices. It is utilized to avoid vibrations from being distributed from one region to another. It lowers noise levels.
- Compression Nut: A ring, often made of rubber or another elastomeric material, that provides the sealing function around the cable when compressed by the sealing nut.
- Rubber Seal (optional): A protective cover that can be placed over the gland body to provide additional environmental protection, such as resistance to water or dust.
What is Double Compression Cable Gland?
A double compression cable gland provides sealing and strain relief at two points: once on the outer sheath of the cable and again on the inner part of the cable, typically through an additional sealing ring or insert. This type of gland offers enhanced protection against environmental factors such as dust, moisture, and chemicals, making it suitable for more demanding applications. Double compression cable glands are ideal for harsh environments and applications with high mechanical stress, ensuring superior strain relief and a more robust seal compared to single compression glands.

The typical components of a double compression cable gland:
- Gland Body: The main part of the gland, housing the other components and providing the overall structure.
- Sealing Nut (Outer Compression Nut): This is tightened to compress the outer seal around the cable’s outer sheath, ensuring a tight seal and providing strain relief.
- Outer Sealing Ring (Outer Compression Ring): Made of rubber or another elastomeric material, this ring provides the first seal around the cable’s outer sheath when compressed by the sealing nut.
- Armor Clamping Ring (Armor Cone/Clamping Cone): This component grips the cable’s armor when the inner compression nut is tightened, providing mechanical strength and continuity.
- Cable gland adapters: It also known as cable gland reducers or cable gland adapters, are components used in cable gland assemblies to connect cables of different sizes or types to equipment
- Inner Sealing Ring (Inner Compression Ring): Similar to the outer sealing ring, but located inside the gland body, providing a seal around the inner sheath of the cable.
- Inner Compression Nut: Tightened to compress the inner sealing ring, securing the inner sheath of the cable and ensuring a secondary seal.
- Entry Thread: The threaded portion of the gland body that is used to secure the gland to the equipment or panel. It comes in various thread types like metric, PG, or NPT.
- Locknut: The lock nuts can be used with other components such as toggle shoe clamp assembly, hand knob assembly, torque thumb screw, and knurled head screw to secure the cable gland.
- Washer: It is a flat washer that is placed between the cable gland’s body and the equipment or enclosure. The seal provides additional sealing and protects the mating surface.
The Differences Between Single Compression and Double Compression Cable Glands
The single-compression cable gland is typically used for light-armoured cables since it provides grip and compression only in one place. Due to this, it does not provide complete protection from moisture or corrosive gases. In contrast, a double-compression cable gland protects both the cable armour and the inner sheath at the same time. Due to the double seal, the cable is weatherproof and protected from moisture. As a result, they are typically used to support heavy armoured cables.
Choosing between a double compression and a single compression cable gland depends on the specific requirements of your installation. For general-purpose applications with moderate environmental challenges, a single compression gland may be sufficient. However, for demanding environments where additional protection and strain relief are needed, a double compression gland is often the better choice. Assessing the environmental conditions, mechanical stress, and budget constraints will help you make the most suitable choice for your application.
At CGS Cable Glands, we offer a wide range of premium quality cable glands including EMC cable glands, IP 68 cable glands, and also offer custom cable glands as per customer specific requirement. Invest in high-quality cable glands that meet your specific requirements to safeguard your equipment from environmental hazards and mechanical stress. Contact us for more information or request a quote for single and double compression cable glands.
